Configuration reference#
Important
This reference is work in progress.
The MESMO configuration is defined via config.yml. As an initial user, you likely do not need to modify the configuration.
Configuration workflow#
An empty config.yml is created during the first runtime of MESMO. To define the local configuration, simply insert and modify configuration parameters from the references below.
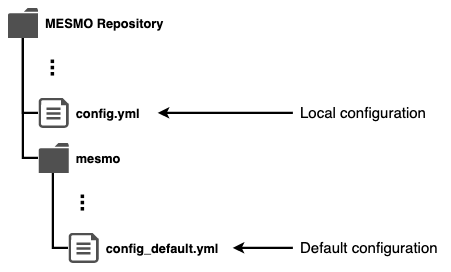
Figure: Configuration file location.
MESMO distinguishes 1) local configuration in config.yml and 2) default configuration in config_default.yml. The local configuration takes precedence over the default configuration. That means, during initialization, get_config() first reads the default configuration from config_default.yml and then redefines any parameters that have been modified in config.yml.

Figure: Configuration initialization workflow.
The following sections serve as a reference for configuration parameters. Please note that key / value pairs are defined in a nested structure for each configuration type. This nested structure needs to be replicated for key / value pairs in config.yml.
Important
Please only modify config.yml, but do not make changes to config_default.yml.
Path configuration#
Default values#
paths:
data: ./data
database: ./data/database.sqlite
results: ./results
additional_data: []
ignore_data_folders: []
cobmo_additional_data: []
Configuration keys#
data: Defines the main data directory, i.e. the location of the CSV input files which are imported bymesmo.data_interface.recreate_database(). Can be given as absolute path or relative path to./¹. Defaults to the data directory that is included with the MESMO repository. If you want to include additional data from other directories, please seeadditional_databelow.database: Defines the file path for the internal SQLITE database. Can be given as absolute path or relative path to./¹. This file will be created bymesmo.data_interface.recreate_database(), if it does not exist.results: Defines the main results directory, i.e. the directory where results outputs are stored. This parameter is used as base path inmesmo.utils.get_results_path(). Defaults to the results directory in the MESMO repository.additional_data: Defines list of supplementary data directories, which are imported in addition to the main data directory bymesmo.data_interface.recreate_database(). Should be defined as list of absolute or relative paths to./¹.ignore_data_folders: Defines a list of directory names that are excluded during import bymesmo.data_interface.recreate_database(). Should be defined as list of folder names to exclude, but does accept full paths.cobmo_additional_data: Defines list of supplementary data directories for thecobmosubmodule, similar toadditional_dataabove.
¹ In the path parameters, ./ denotes the MESMO repository base directory as reference for relative path definitions.
Using additional data directories#
As an example, additional data from folders supplementary_data and project_data adjacent to the MESMO repository base directory can be defined with the following configuration snippet:
paths:
additional_data: [
./../supplementary_data,
./../project_data
]
Optimization solver configuration#
Default values#
optimization:
solver_name: highs
solver_interface: direct
show_solver_output: true
time_limit:
Configuration keys#
solver_name: Defines the optimization solver. Choices are ‘highs’, ‘gurobi’ or any valid solver name for CVXPY. Solver name should be defined in lower caps.solver_interface: Defines the interface for sending the optimization problem to the solver. Choices are ‘direct’ or ‘cvxpy’. If ‘direct’, MESMO will use a direct solver interface, which is currently implemented for HiGHS and Gurobi. If no direct solver interface is available for the selected solver, MESMO will automatically fall back to CVXPY. If ‘cvxpy’, MESMO will always use CVXPY without checking for a direct solver interface. If not defined, will use ‘direct’.time_limit: Solver time limit in seconds. If not defined, the value is set to infinite. Currently only implemented for HiGHS, Gurobi and CPLEX.show_solver_output: Choices are ‘true’ or ‘false’. If ‘true’, activate verbose solver output. If ‘false’, silence any solver outputs.
Setting CPLEX as optimization solver#
As an example, CPLEX can be defined as the optimization solver with the following configuration snippet:
optimization:
solver_name: cplex
solver_interface: cvxpy
Note that CPLEX is interfaced through CVXPY, because there is currently no direct interface implemented in MESMO. This requires CPLEX to be installed as per CVXPY instructions.
Multiprocessing configuration#
MESMO enables multiprocessing, i.e. parallel processing, of subtasks that are enabled for parallelization via mesmo.utils.starmap(). This can be useful when running very large scenarios, but requires additional computational overhead for starting up and maintaining a pool of parallel workers. Therefore, this feature is disabled by default and not recommended when running small test cases.
Default values#
multiprocessing:
run_parallel: false
cpu_share: 1.0
Configuration keys#
run_parallel: Enables / disables multiprocessing. Disabled by default and not recommended when running small scenarios.cpu_share: Defines the share of CPU cores to be used for parallel processing. Can be used to limit the system loading, e.g. on shared workstations.
Logging and tests configuration#
Default values#
logs:
level: info
format: '%(asctime)s | %(levelname)s | %(message)s'
tests:
scenario_name: singapore_6node
thermal_grid_scenario_name: singapore_tanjongpagar
Configuration keys#
level: Defines the logging level for the Python logging facility. Choices:debug,info,warn. All log messages at or above the selected log level are printed, in the following orderdebug<info<warn.format: Defines the format of the log message output. See here and here for additional information on how to define the format string.scenario_name: Defines the scenario which is used when running automated testing scripts in thetestsdirectory and some of the example scripts in theexamplesdirectory.thermal_grid_scenario_name: Defines the scenario which is used for thermal-grid-related tests when running automated testing scripts in thetestsdirectory.
Plot configuration#
Default values#
plots:
matplotlib_style: seaborn-colorblind
matplotlib_colormap: viridis_r
matplotlib_font_family: ['Arial', 'Helvetica']
matplotlib_figure_size: [7.0, 4.0]
plotly_font_family: Arial
plotly_font_size: 15
plotly_figure_width: 1000
plotly_figure_height: 500
file_format: png
add_basemap: false
show_basemap_attribution:
Configuration keys#
matplotlib_style: Defines the style template for matplotlib plots.matplotlib_colormap: Defines the colormap for matplotlib plots.matplotlib_font_family: Defines the fonts for matplotlib plots.matplotlib_figure_size: Defines the figure size for matplotlib plots in inch.plotly_font_family: Defines the font for plotly plots.plotly_font_size: Defines the font size for plotly plots.plotly_figure_width: Defines the figure width for plotly plots in pixels.plotly_figure_height: Defines the figure height for plotly plots in pixels.file_format: Defines the file format for matplotlib / plotly plots.add_basemap: If True, add basemap layer to static grid plots for orientation. Requires installation ofcontextily.show_basemap_attribution: If True, show copyright notice for basemap.